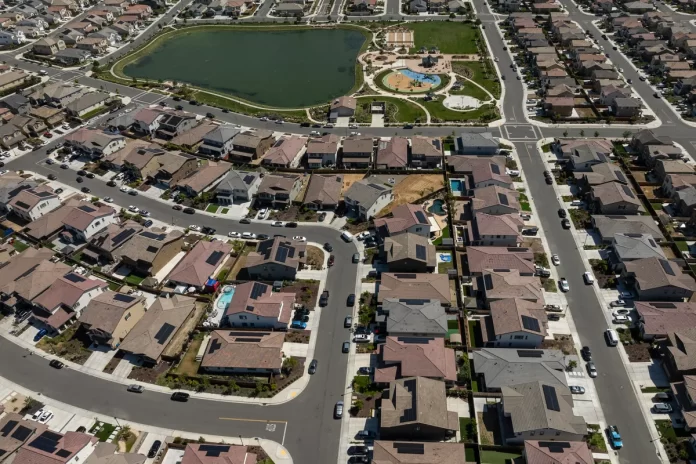
One of California’s many socioeconomic divisions is homeownership.
California has the nation’s second-lowest percentage of residents living in homes that they or their families own — 55.5%, one percentage point higher than New York. But those owners are sitting on immense equity, roughly $2 trillion, thanks to the state’s highest-in-the-nation home prices.
Last month, the median price of single-family home in California was $868,150, according to the California Association of Realtors, more than twice the national median.
“Monthly payments for a newly purchased mid-tier home — including mortgage, taxes and homeowners’ insurance — have increased dramatically over the last couple of years,” the nonpartisan Legislative Analyst’s Office noted in a recent report. “Payments for a mid-tier home were nearly $6,000 a month in June 2024 — an 84% increase since January 2020. Payments for a bottom-tier home were over $3,600 per month — an 89% increase since January 2020.
“Annual household income needed to qualify for a mortgage on a mid-tier California home in June 2024 was about $239,000 — over two times the median California household income in 2022 ($95,500),” the report continued.
There is, as with other economic indices, a very strong racial component to California homeownership.
Public Policy Institute of California researchers this week declared that “persistent racial homeownership gaps run deep across the state — and these gaps have contributed to substantial wealth disparities across demographic groups.
“In 2023,” PPIC fellows Marisol Cuellar Mejia, Hans Johnson and Julien Lafortune continued, “Latino homeownership rate stood at 45.9%, or 18.5 points below that of white households. The Black homeownership rate was even more worrisome at 36.6%, or 27.9 points below the rate for white households. Meanwhile, at 61.5%, the rate among Asian Americans was only 3 percentage points below.”
Given the prominence of home equity in family net worth, the ownership gap strongly affects what economists call “generational wealth.”